Dual Ring Topology And Star Topology
Dual Ring Topology

Dual ring topology is a computer network architecture that consists of two rings, each carrying traffic in the opposite direction. This design provides a level of redundancy and reliability that is not possible with a single ring topology. In this article, we will explore the features, advantages, and disadvantages of dual ring topology.
Features of Dual Ring Topology:
Redundancy: Dual ring topology provides redundancy, which means that if one of the rings fails, the other ring can take over the traffic.
Fault tolerance:
Dual ring topology is fault-tolerant, meaning that if there is a problem with one of the rings, the network can still function using the other ring.
High reliability:
The redundancy and fault tolerance provided by the dual ring topology make it highly reliable. If there is a problem with one of the rings, the other ring can take over without any disruption to the network.
Bidirectional traffic:
Dual ring topology allows for bidirectional traffic flow, which means that data can be transmitted in both directions simultaneously.
Efficient data transfer:
Dual ring topology provides efficient data transfer because the data can be transmitted simultaneously on both rings.
Advantages of Dual Ring Topology:
High reliability:
Dual ring topology provides a high level of reliability because of the redundancy and fault tolerance it offers. This means that the network can continue to function even if one of the rings fails.
Efficient data transfer:
Dual ring topology allows for efficient data transfer because data can be transmitted simultaneously on both rings.
Cost-effective:
Dual ring topology is cost-effective because it does not require expensive switches or hubs to connect the devices.
Scalability:
Dual ring topology is scalable, which means that it can be easily expanded to accommodate additional devices.
Disadvantages of Dual Ring Topology:
Complexity:
Dual ring topology is more complex than other topologies, such as star or bus, which can make it more difficult to set up and maintain.
Limited distance:
Dual ring topology has limited distance capabilities, which means that it is not suitable for large networks that are spread out over a wide geographic area.
Limited number of devices:
Dual ring topology has a limited number of devices that can be connected to each ring, which can be a problem for larger networks.
Cost of installation:
The installation of dual ring topology can be expensive because of the need for specialized equipment and cabling.
Conclusion:
Dual ring topology is a reliable and efficient network topology that provides redundancy and fault tolerance, allowing the network to continue functioning even if one of the rings fails. It is a cost-effective option that is scalable and can be easily expanded to accommodate additional devices. However, it is more complex than other topologies, has limited distance capabilities, a limited number of devices, and can be costly to install. It is important to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of dual ring topology before choosing it as the network topology for your organization.
Star Topology
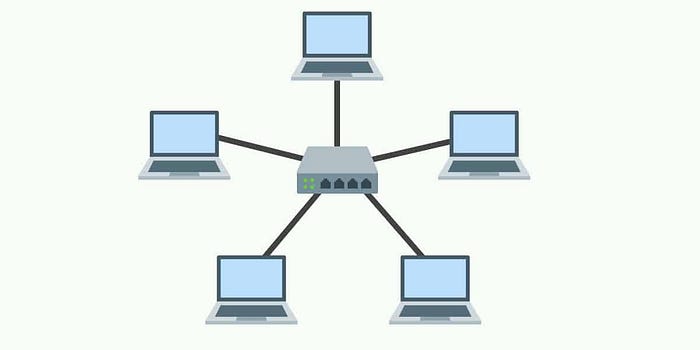
In computer networking, topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of devices connected to a network. One of the most common topologies used in networks is the star topology. It is widely used in LAN (local area network) and WAN (wide area network) configurations. In this article, we will discuss the features, advantages, and disadvantages of the star topology.
Features of Star Topology:
The star topology is a type of network topology where all devices are connected to a central device called a hub or switch. Each device has its own connection to the hub or switch, forming a point-to-point connection between the device and the hub or switch. The following are some features of the star topology:
Centralization:
The star topology is centralized, which means that all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. This makes it easy to manage the network, as all devices are connected to a single point.
Scalability:
The star topology is highly scalable. New devices can be easily added to the network by connecting them to the central hub or switch.
Reliability:
The star topology is a reliable topology because if one device fails, it does not affect the rest of the network. The faulty device can be easily removed or replaced without affecting the network’s functionality.
Advantages of Star Topology:
The star topology has several advantages over other network topologies. Some of the key advantages are:
Easy to install:
The star topology is easy to install and configure. Devices can be added or removed without affecting the rest of the network.
Centralized management:
As all devices are connected to a central hub or switch, network management is easier and more efficient.
Fault tolerance:
The star topology is fault-tolerant, which means that if one device fails, it does not affect the rest of the network.
High performance:
The star topology provides high network performance, as each device has its own dedicated connection to the central hub or switch.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
The star topology also has some disadvantages, which include:
Single point of failure:
The central hub or switch is a single point of failure in the network. If the hub or switch fails, the entire network will be affected.
Cost:
The star topology can be more expensive than other topologies, as each device needs its own connection to the central hub or switch.
Limited scalability:
While the star topology is highly scalable, it is still limited by the capacity of the central hub or switch.
Conclusion:
The star topology is a widely used network topology that provides several advantages, including easy installation, centralized management, fault tolerance, and high performance. However, it also has some disadvantages, such as a single point of failure, cost, and limited scalability. When choosing a network topology, it is important to consider the specific needs of the network and the trade-offs between different topologies.
Bug Zero is a bug bounty, crowdsourcing platform for security testing. The platform is the intermediatory entity that enables client organizations to publish their service endpoints so that bug hunters (security researchers / ethical hackers) registered in the platform can start testing the endpoints without any upfront charge. Bug hunters can start testing as soon as a client organization publishes a new program. Bug Zero also offers private bug bounty programs for organizations with high-security requirements.

Bug Zero is available for both hackers and organizations.
For organizations and hackers, register with Bug Zero for free, and let’s make cyberspace safe.
